LMMs-Lab
Feeling and building multimodal intelligence


LMMs-Eval
We're on an exciting journey toward creating Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), much like the enthusiasm of the 1960s moon landing. This journey is powered by advanced large language models (LLMs) and large multimodal models (LMMs), which are complex
systems capable of understanding, learning, and performing a wide variety of human tasks.
To gauge how advanced these models are, we use a variety of evaluation benchmarks. These benchmarks are tools that help us understand the capabilities of these models, showing us how close we are to achieving AGI.
To address this challenge, we introduce lmms-eval, an evaluation framework meticulously crafted for consistent and efficient evaluation of LMM.
LLaVA-NeXT
We expanded the LLaVA-NeXT series with recent stronger open LLMs, reporting our findings on more capable language models:
We maintain an efficient training strategy like previous LLaVA models. We supervised finetuned our model on the same data as in previous LLaVA-NeXT 7B/13B/34B models. Our current largest model LLaVA-NeXT-110B is trained
on 128 H800-80G for 18 hours.
With stronger LLMs support, LLaVA-NeXT achieves consistently better performance compared with prior open-source LMMs by simply increasing the LLM capability. It catches up to GPT4-V on selected benchmarks.
We report detailed ablations, including architectural modifications, enlarged visual tokens, and varied training strategies, to explore potential improvements in LLaVA-NeXT's performance.

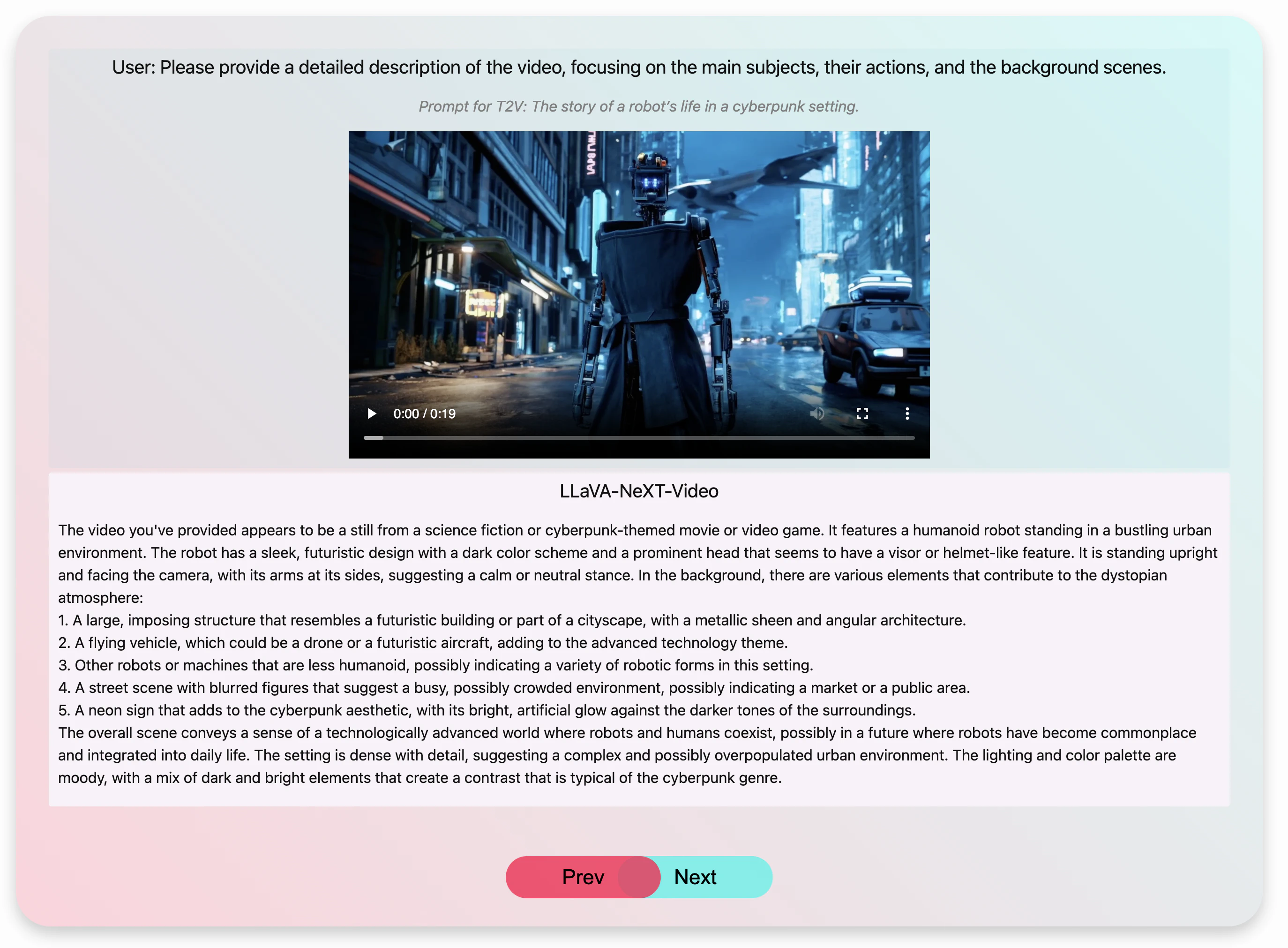
LLaVA-NeXT Video
We explore LLaVA-NeXT's capabilities in video understanding tasks, highlighting its strong performance. Key improvements include:
SoTA Performance! Without seeing any video data, LLaVA-Next demonstrates strong zero-shot modality transfer ability, outperforming all the existing open-source LMMs (e.g., LLaMA-VID) that have been specifically
trained for videos. Compared with proprietary ones, it achieves comparable performance with Gemini Pro on NextQA and ActivityNet-QA.
Strong length generalization ability. Despite being trained under the sequence length constraint of a 4096-token limit, LLaVA-Next demonstrates remarkable ability to generalize to longer sequences. This
capability ensures robust performance even when processing long-frame content that exceeds the original token length limitation.
DPO pushes performance. DPO with AI feedback on videos yields significant performance gains.
LongVA
Gemini has amazed the world with its capability to understand hour-long videos. However, we still lack an open-source alternative with similar capabilities. Our latest research presents an innovative solution towards long video LMM, shifting the focus
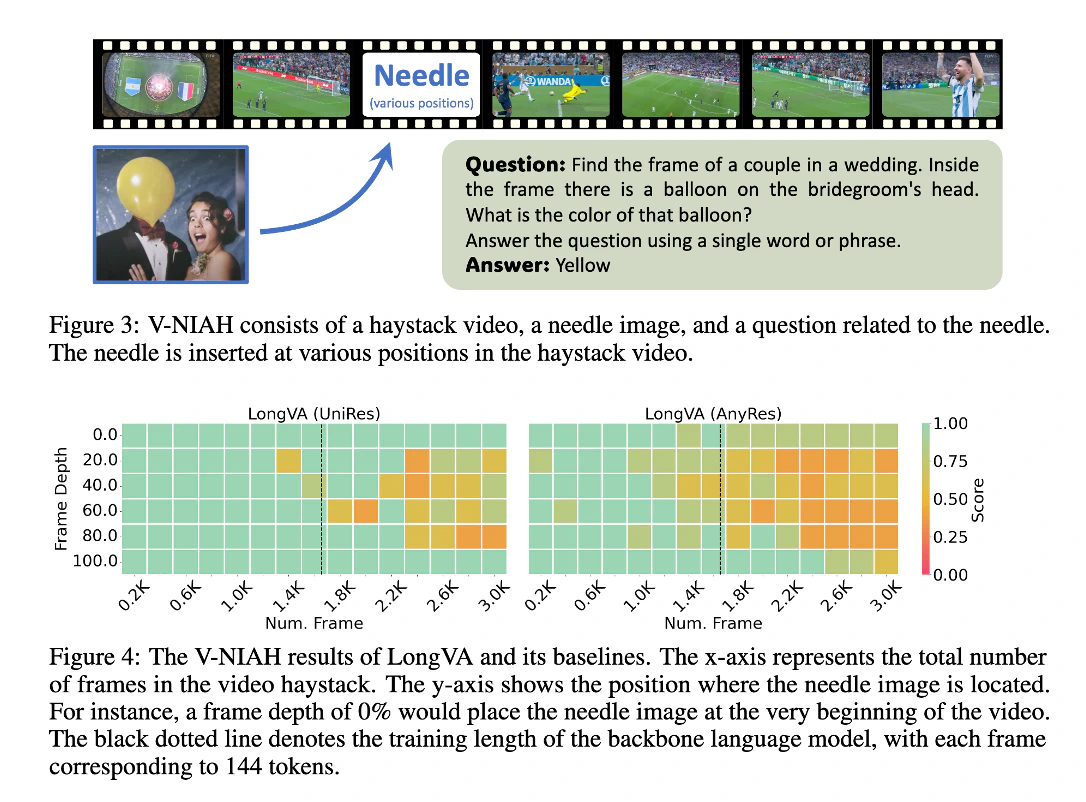
from reducing visual tokens per frame to leveraging the long context capabilities of language models. Here, we present our SoTA video model, Long Video Assistant (LongVA), and our novel benchmark, Visual Needle-In-A-Haystack
(V-NIAH).
Long Context Transfer We discovered and verified that the long context capability of language models can be directly transferred to the video domain in modality-aligned multi-modal models. On V-NIAH, LongVA
is the only open-source model capable of accurately retrieving visual information from inputs with 2000 frames or more than 200K visual tokens.
UniRes We proposed UniRes, a unified visual encoding scheme that encodes both images and videos. In UniRes, a video is encoded the same as multiple image crops in a sequence. Leveraging the Long Context
Transfer property and UniRes, LongVA exhibits superior zero-shot performance in video tasks without any video-specific training data.
SoTA Performance LongVA achieves state-of-the-art performance on the comprehensive Video-MME benchmarks among 7B models. Its performance increases with denser sampling of video frames. We also conduct careful
experiments to ablate where it improvements come from.
